Have you ever stopped to think about how your trusty microwave oven works its magic? How it heats up your leftover pizza in seconds or warms your morning coffee to the perfect temperature? It’s all thanks to the wavelength of the microwaves that are produced inside the oven, but what exactly is the cooking frequency of a microwave oven with a 12cm wavelength?
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation that have wavelengths ranging from one millimeter to one meter. When these waves come into contact with water molecules in food, they cause them to vibrate rapidly, creating heat and cooking the food. However, for this process to work efficiently, the microwaves need to be produced at a specific frequency that matches the resonant frequency of water molecules.
Enter the cooking frequency of a microwave oven – this refers to the frequency at which microwaves are produced inside the oven. So, if your microwave has a 12cm wavelength, its cooking frequency will be approximately 2.5 GHz.
But why does this matter? Knowing your microwave’s cooking frequency can help you determine optimal cooking times for different types of food and troubleshoot any issues like uneven heating or hot spots.
So next time you pop something into your microwave oven, take a moment to appreciate the science behind it and how its specific cooking frequency is essential for heating up your meals quickly and efficiently.
Contents
What is the Wavelength of a Microwave Oven?
Microwave ovens are a marvel of modern technology, allowing us to quickly and easily heat up our food with just the push of a button. But what is the secret behind their efficiency? It all comes down to the wavelength and frequency of their electromagnetic waves.
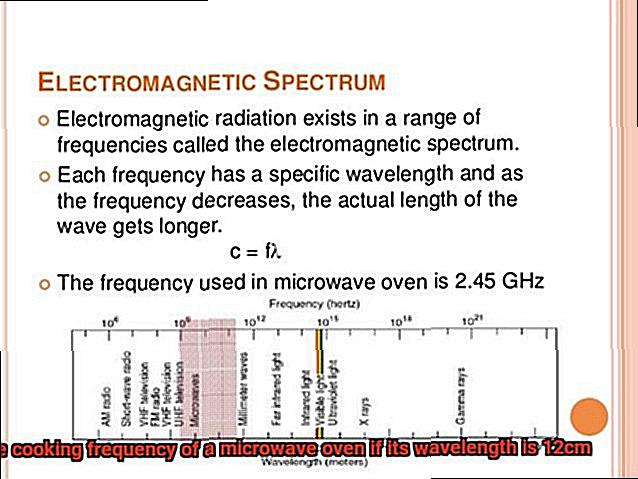
Electromagnetic waves, including microwaves, have both a wavelength and a frequency. The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave, while the frequency is how many waves pass a given point in one second. For microwaves, the typical wavelength is around 12 centimeters, corresponding to a frequency of about 2.45 GHz.
This specific frequency is chosen because it allows for efficient heating of water molecules. Most foods contain water molecules, which are polarized with a positive and negative end. When exposed to microwaves with the right frequency, these water molecules vibrate rapidly, generating heat that cooks the food from the inside out.
The magnetron, an essential component of any microwave oven, generates these microwaves by converting electrical energy into electromagnetic radiation in the microwave range. The microwaves are then emitted into the cooking chamber of the oven, where they interact with the food.
But why does this specific wavelength work so well for cooking? It all has to do with how different frequencies interact with different materials. Microwave ovens need a frequency that can easily penetrate through most common materials used in cooking without being absorbed or reflected back. The 2.45 GHz frequency does just that, allowing for efficient heating without damaging the food or the oven itself.
It’s important to note that not all microwave ovens operate at exactly 2.45 GHz. Some may vary slightly within the microwave range, which can impact cooking times and temperatures. Manufacturers typically provide instructions on how to adjust cooking times and settings accordingly.
How to Calculate the Cooking Frequency of a Microwave Oven
Microwave ovens have become a staple in many households due to their convenience and speed. However, to truly master the art of microwave cooking, it’s important to understand the cooking frequency of your oven. This is the frequency at which the microwaves oscillate and interact with food, ultimately determining how quickly and evenly it cooks.
To calculate the cooking frequency of a microwave oven, we first need to define frequency and wavelength. Frequency refers to the number of waves that pass through a given point per second, while wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points on a wave. Microwave ovens operate at a specific frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz).
The formula for calculating the cooking frequency of a microwave oven is simple yet powerful:
frequency = speed of light / wavelength
The speed of light is a constant value of approximately 299,792,458 meters per second. To use this formula for microwaves, we need to convert the wavelength from centimeters to meters by dividing by 100. For example, if our microwave oven has a wavelength of 12cm, we can convert it to 0.12 meters.
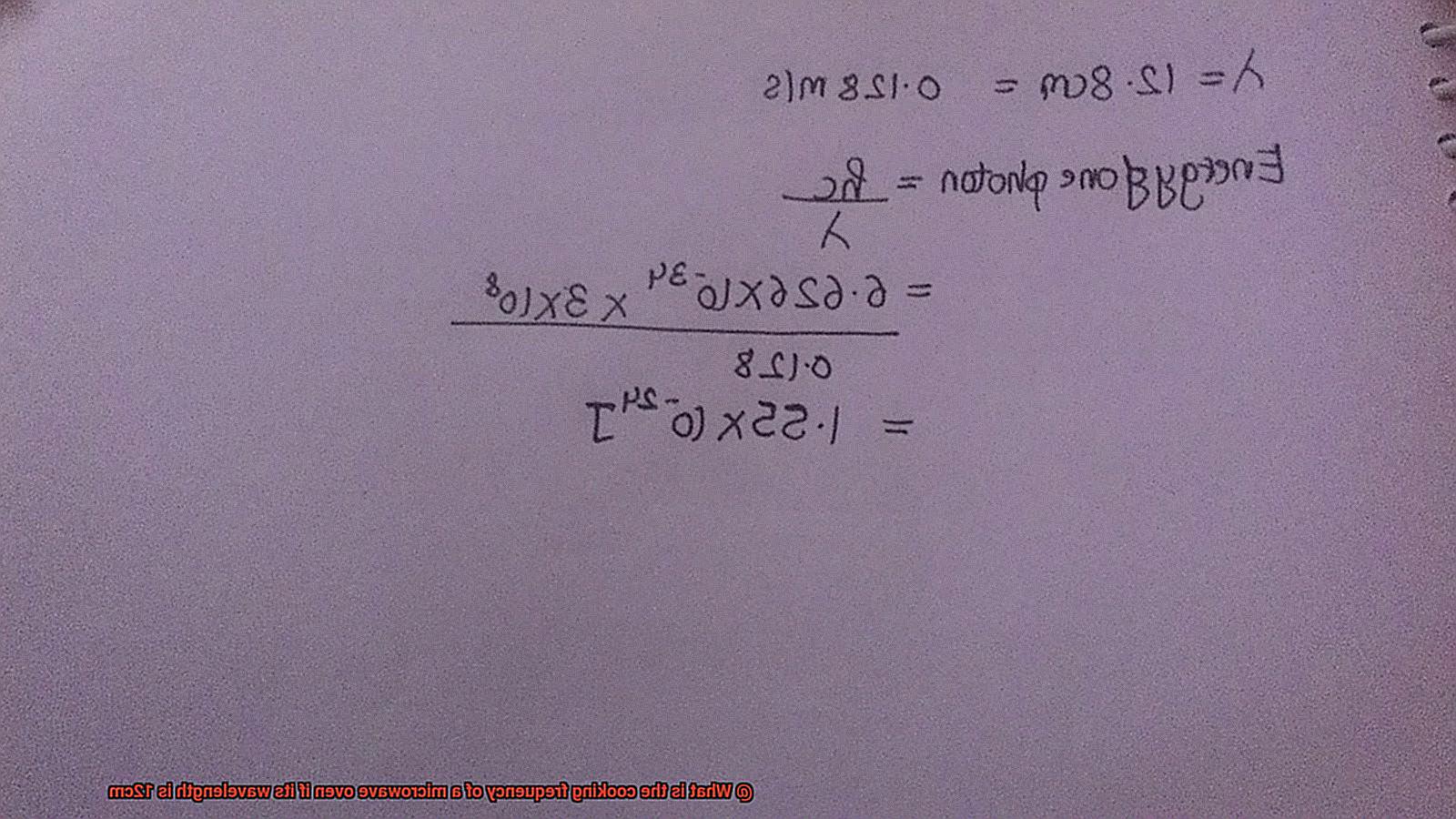
Now that we have the necessary values, we can calculate the cooking frequency of our microwave oven:
frequency = 299,792,458 / 0.12
frequency = 2.498 GHz
This means that the microwaves in our oven oscillate at a rate of 2.498 billion times per second. Understanding this frequency allows us to adjust cooking times and settings for optimal results.
Knowing the cooking frequency of your microwave oven can also be helpful when troubleshooting issues. For instance, if your food isn’t heating evenly or taking longer than expected to cook, it may be due to a malfunctioning magnetron (the component responsible for generating microwaves) operating at a different frequency than intended.
The Speed of Light and Its Role in Calculations
Microwave ovens are a modern marvel that has transformed the way we cook our food. But have you ever stopped to wonder how these magical machines work? Well, one crucial element in the process is the speed of light. That’s right, this fundamental constant in physics plays a significant role in determining the frequency of microwaves, which is essential in cooking your food.
The speed of light is defined as the rate at which electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum, and it’s approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (m/s). This speed is so fast that it has become a benchmark for measuring the speed of other objects. In the case of microwaves, the speed of light is instrumental in determining their frequency.
Frequency is the number of complete cycles a wave completes in one second, measured in hertz (Hz). The frequency of a microwave oven determines how many times per second an electromagnetic wave passes through your food, causing its molecules to vibrate and generate heat. This concept might seem abstract at first glance, but understanding it can help you adjust cooking times and troubleshoot issues for optimal results.
The relationship between wavelength and frequency is given by the formula: frequency = speed of light / wavelength. This formula means that if we know the wavelength of a microwave oven, we can easily calculate its frequency using the speed of light constant. For example, let’s say a microwave oven has a wavelength of 12 cm. In that case, its frequency can be calculated as follows:
Frequency = Speed of Light / Wavelength
Frequency = 299,792,458 m/s / 0.12 m
Frequency = 2,498,270,483 Hz
This calculation shows that the cooking frequency of a microwave oven with a wavelength of 12 cm is approximately 2.5 GHz (gigahertz). In other words, the electromagnetic wave passes through your food 2.5 billion times per second, causing its molecules to vibrate and generate heat rapidly.
The Cooking Frequency of a Microwave Oven with a Wavelength of 12cm
The cooking frequency of a microwave oven, directly related to its wavelength, is at the heart of this question. Simply put, wavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a wave. In the case of a microwave oven with a 12cm wavelength, the cooking frequency is approximately 2.5 GHz or 2.5 billion times per second.
Why does this matter? Well, when you switch on your microwave, it produces electromagnetic waves that penetrate your food and cause water molecules to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat and cooks your food. The cooking frequency determines how efficiently this happens. The higher the cooking frequency, the more energy is transferred to your food, leading to faster and more even cooking.
However, different foods need different cooking frequencies for optimal results. High water content foods such as vegetables and meats require a higher cooking frequency than frozen foods or baked goods. To achieve ideal results, adjusting the power output of your microwave oven based on the type and amount of food being cooked is crucial.
Factors that Affect Cooking Time and Temperature in Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens are a go-to kitchen appliance for quick and easy meal preparation. However, achieving optimal cooking time and temperature can be tricky due to various factors that affect the process.
Wattage is a significant factor in microwave cooking. Higher wattage ovens cook food faster than lower wattage ones. So, if you’re in a hurry, a 1000-watt microwave oven will cook your food faster than an 800-watt one.
The size and shape of the food item being cooked also determine cooking time and temperature. Smaller and thinner food items cook faster than larger and thicker ones. Irregularly shaped foods may require additional stirring or turning during cooking to ensure even cooking.
The type of container used to cook food in a microwave oven can also affect the cooking process. Microwave-safe containers made of glass, plastic, or ceramic materials are suitable for use in microwave ovens. But avoid using metal containers or utensils in the microwave as they can cause sparks and damage to the appliance.
Additionally, starting temperature can affect cooking time and temperature in microwave ovens. Foods that are at room temperature or warm will cook faster than those that are cold or frozen. Thawing your food item or letting it reach room temperature before placing it in the microwave oven can make a significant difference in cooking time.
Understanding the Cooking Frequency for Optimal Results
Understanding the cooking frequency of your microwave oven can help you avoid these culinary mishaps and achieve optimal results.
Frequency in microwaves refers to the number of times the electromagnetic waves produced by the oven oscillate per second. For a typical microwave oven, the cooking frequency is around 2.45 GHz, which means that the electromagnetic waves produced by the oven oscillate at a rate of 2.45 billion times per second. This specific frequency was chosen because it causes water molecules in food to vibrate, generating heat and cooking your food.
But why is knowing your microwave’s cooking frequency important? Understanding this crucial aspect of your appliance can mean the difference between perfectly cooked dishes and frustrating mishaps. The frequency determines how evenly your food is heated and how quickly it cooks.
Foods with higher water content, such as vegetables or soups, will cook faster in a microwave with a higher frequency since the frequency causes water molecules to vibrate more quickly. Additionally, some recipes may specify a certain cooking time based on the wattage and frequency of the microwave being used. By understanding your microwave’s frequency, you can ensure that you are following recipes correctly and achieving the desired results.
It’s also worth noting that wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional. As the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases. In the case of a microwave oven with a frequency of 2.45 GHz, the wavelength is approximately 12 cm.
Different Types of Food and Materials Suitable for Microwaves
Microwaving has become a staple in many kitchens, providing a quick and easy way to cook or heat up food. However, it’s important to know which types of food and materials are safe to use in the microwave to prevent damage or potential health hazards. Here are five sub-sections that explain the different types of food and materials suitable for microwaving.
Vegetables
Vegetables are an excellent option for microwaving as it helps retain their nutrients better than other cooking methods. The high-frequency waves of microwaves quickly heat up the water molecules in vegetables, leading to fast and even cooking. However, some vegetables like potatoes require piercing with a fork or covering with a lid to prevent steam buildup that could cause them to explode.
Popcorn
For popcorn lovers, microwavable popcorn bags release steam when heated, resulting in fluffy and delicious popcorn. However, it’s crucial to follow the instructions on the packaging carefully, as overheating can cause the bag to catch fire.
Meat
Cooking meat in a microwave can be challenging as it can easily become tough and dry. It’s essential to use the right power settings and cooking times to ensure that the meat is cooked through but still tender. It’s also crucial to let the meat rest for a few minutes after cooking to allow the juices to redistribute.
Glass and ceramics
Glass and ceramic dishes are safe to use in the microwave, but it’s critical to check that they aren’t chipped or cracked as they could break during cooking. It’s also important not to use dishes with metallic elements or air pockets that can cause them to spark or shatter when heated.
Plastic containers labeled as microwave-safe
Many people rely on plastic containers for reheating leftovers or cooking meals in the microwave. It’s crucial to use plastic containers labeled as microwave-safe because they’re designed not to release harmful chemicals into your food. However, plastic wrap or containers not labeled as microwave-safe should be avoided.
Safety Tips for Using Microwaves
Microwaves have transformed the way we cook and heat up food quickly. However, they can also pose a safety risk if not used correctly. To help you use your microwave safely, here are some crucial safety tips to keep in mind.
Firstly, read the manual carefully. It may seem tedious, but it’s essential to understand how to use the appliance properly. The manual will provide useful information about the microwave’s features, what kind of containers and food you can cook in it, and how to avoid any potential hazards.
Secondly, only use microwave-safe containers. Using plastic or metal containers that are not labeled as microwave-safe can lead to fires, explosions, and release harmful chemicals into your food. Always make sure you’re using a container that is specially designed for microwave use.
Thirdly, keep your microwave clean. Food residues and spills can cause fires and damage the appliance. Make sure to wipe down the microwave regularly with a damp cloth.
Fourthly, be cautious when heating liquids. Overheating liquids in the microwave can cause them to boil over or explode, which can lead to burns and scalds. Always stir liquids before heating them and use a thermometer to check the temperature.
Fifthly, use oven mitts or potholders when handling hot dishes from the microwave. Even if the container feels cool to touch from the outside, the food inside can still be extremely hot.
Lastly, supervise children when they are around the microwave. Children should not use microwaves without adult supervision. Teach them how to use it safely and explain why it’s essential to follow safety guidelines.
D9_2qtD8flo” >
Conclusion
To sum up, the cooking frequency of a microwave oven is the key factor that determines how fast and effectively it cooks your food. At a wavelength of 12cm, the cooking frequency of an average microwave oven is about 2.5 GHz. This particular frequency works by making water molecules in your food vibrate rapidly, thereby generating heat and cooking your meal from the inside out.
Knowing your microwave’s cooking frequency can be advantageous when adjusting cooking times and settings for optimal results. Furthermore, it can be useful in troubleshooting problems like uneven heating or hot spots. It’s worth noting that different types of foods require varying cooking frequencies for ideal outcomes, making it essential to adjust power output based on what you’re cooking.
Microwaves are undoubtedly convenient appliances in any kitchen, but they can pose safety concerns if not used correctly. Reading the manual carefully, using only microwave-safe containers, keeping the appliance clean, being cautious when heating liquids, using oven mitts or potholders when handling hot dishes, and supervising children around the microwave are all crucial steps to ensure safety.