Are you aware of the invisible energy that surrounds us all the time? Yes, we’re talking about microwave radiation. It’s present in our daily lives, from heating up our food to providing us with seamless communication through cell phone signals. But have you ever wondered how far this energy can travel and what impact it has on us?
Microwave radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has a wide range of frequencies and wavelengths. It can travel through different materials, but its ability to penetrate depends on the density of the material and wavelength.
When it comes to microwave ovens, the radiation travels only a short distance before being absorbed by the food and heating it up. But for cell phone signals, microwave radiation can travel much farther than we think.
In this blog post, we’ll take you on a journey into the fascinating world of microwave radiation. We’ll explore how this energy interacts with various materials and what factors can affect its propagation. Along with that, we’ll also discuss some precautions that we should take to protect ourselves from excessive exposure.
So get ready to dive deep into this topic and learn everything you ever wanted to know about how far microwave radiation can travel and its impact on our lives.
Contents
Definition of Microwave Radiation
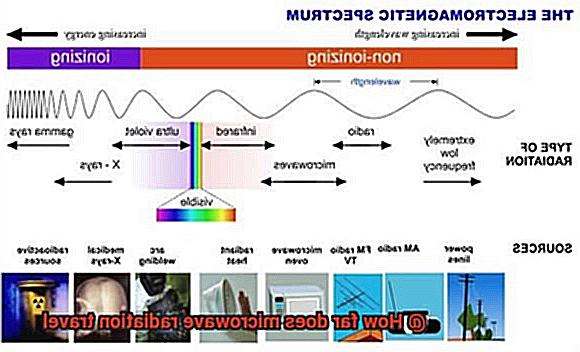
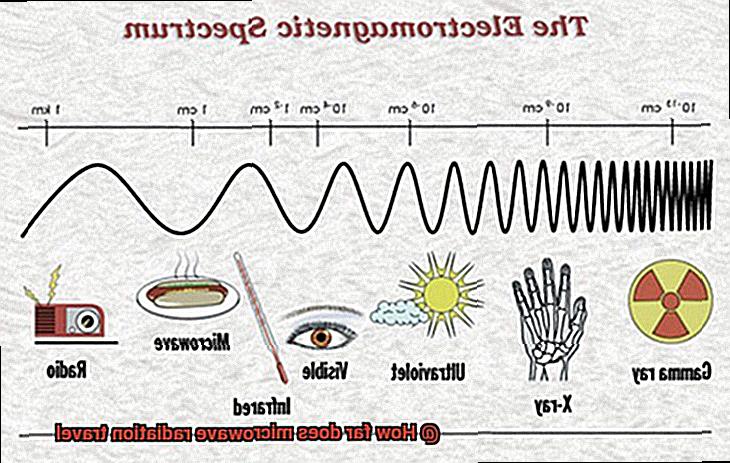
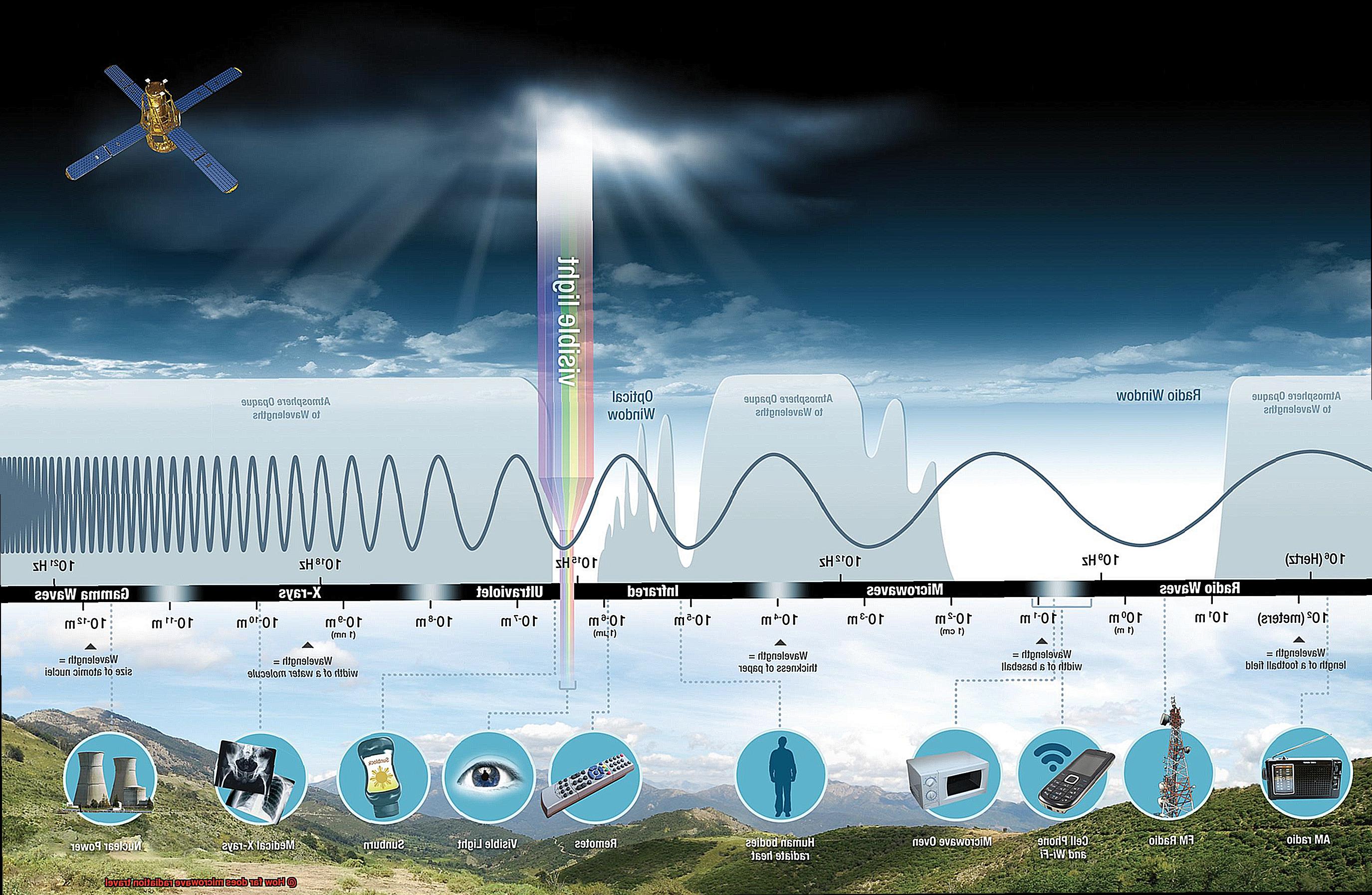
Microwave radiation, a type of electromagnetic radiation, is more than just the secret ingredient behind the quick and easy meal prep of our beloved microwave ovens. This type of radiation is defined by its wavelength range between 1 millimeter and 1 meter and its frequency range typically between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. It falls in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves between radio waves and infrared radiation. The term “microwave” comes from the fact that it has a shorter wavelength than radio waves but longer wavelengths than infrared radiation.
Microwave radiation is used for a wide range of purposes beyond cooking. For example, it is used for satellite communication, cellular phones, and radar systems. Due to its ability to penetrate certain materials like glass and plastic, it has become an important tool for communication purposes through satellite dishes. However, it can also be absorbed by dense materials like concrete and stone.
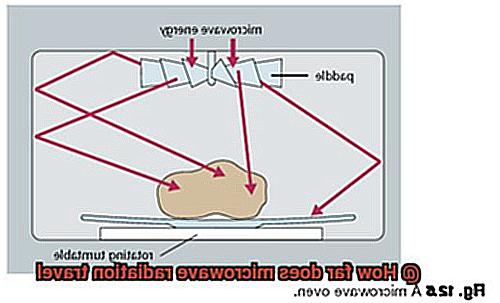
The quick heating power of microwave radiation in microwave ovens comes from the rapid vibrations of water molecules in the food, generating heat that cooks the food evenly and efficiently. In addition to cooking, microwave radiation has become an essential part of modern communication technology.
While microwave radiation is generally safe at low levels, exposure to high levels can be harmful. It’s important to follow safety guidelines when using microwave ovens or other sources of microwave radiation. Since some people may be more sensitive to microwave radiation than others, it’s important to be aware of any symptoms or discomfort that may arise from exposure.
Frequency and Wavelength of Microwave Radiation
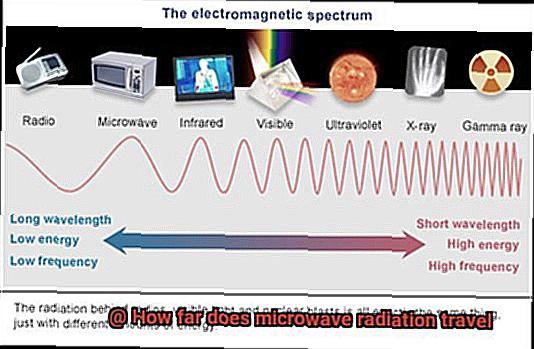
Firstly, let’s get familiar with the basics. Microwave radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls within the frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz, with a wavelength spanning from 1 millimeter to 1 meter. This unique type of radiation is commonly used in various applications such as communication, radar, and cooking because it can penetrate through materials like glass, plastic, and ceramics without causing damage.
Now, let’s dive into how the frequency and wavelength of microwave radiation impact its ability to travel long distances. Higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and are more easily absorbed by materials, limiting their range. Conversely, lower frequencies have longer wavelengths and travel further distances with less absorption by materials.
For instance, microwave ovens use a frequency of around 2.45 GHz, corresponding to a wavelength of about 12 centimeters. This frequency is ideal for heating food items because it is efficiently absorbed by water molecules. However, its range is restricted to just a few meters, making it unsuitable for long-distance communication or radar applications.
On the other hand, microwave communication systems operate at frequencies between 6 and 60 GHz and corresponding wavelengths ranging from 5 to 0.5 centimeters. These frequencies have a larger range than those used in microwave ovens but still experience limitations due to atmospheric absorption and the curvature of the Earth’s surface.
Therefore, understanding the frequency and wavelength of microwave radiation is critical to determine its potential uses. Microwave radiation is best suited for short-range communication and cooking applications. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves and light are better suited for long-distance communication and observation.
Sources of Microwave Radiation
Microwave radiation is a fascinating and powerful form of electromagnetic radiation that has transformed our world. From communication systems to household appliances, there are numerous sources of this energy that we interact with on a daily basis.
At the forefront of microwave radiation are man-made technologies like mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, and satellite communication systems. These devices use microwave radiation to transmit data and emit significant amounts of it. They have become essential tools for communication in our modern society.
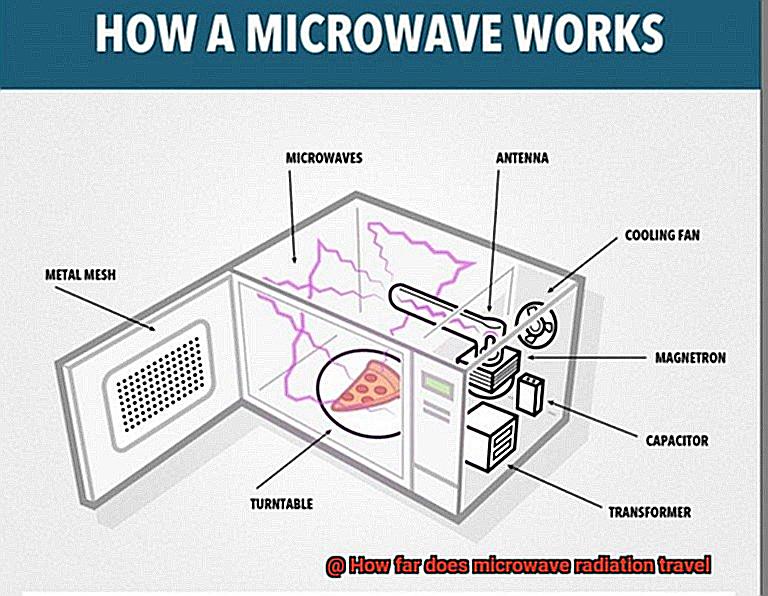
In addition to these technologies, household appliances like microwave ovens are also major sources of microwave radiation. The microwaves generated by these appliances are absorbed by the food, converting them into heat and making cooking fast and efficient.
While man-made technology is the primary source of microwave radiation, natural sources like the sun, stars, and cosmic particles also emit low levels of this energy. Though their impact on human health is relatively low, prolonged exposure can still have an impact over time.
Even electronic devices like computers and televisions emit low levels of microwave radiation. Though their levels are relatively low compared to other sources, prolonged exposure can still pose negative health effects.
Factors Affecting How Far Microwave Radiation Can Travel
Firstly, let’s talk about frequency. Microwave radiation is measured in Hertz, which indicates the number of waves that pass a given point in a second. The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength – and the further the radiation can travel. It’s like throwing a ball – a larger ball (lower frequency) is easier to throw and can travel further than a smaller ball (higher frequency). However, lower frequency microwaves also have lower energy levels, which can impact their ability to penetrate certain materials.
Another key factor is power. Just like with sound, a higher power source can transmit microwaves over longer distances than a lower power source. High power sources produce more intense electromagnetic fields that can overcome obstacles and interference. It’s like yelling – if you yell loudly (higher power), your voice will carry further.
Lastly, the surrounding environment plays a crucial role. Obstacles such as buildings and trees can block or scatter microwaves, reducing their range. Additionally, atmospheric conditions such as rain and fog can absorb or reflect microwaves, further limiting their range.
To summarize, understanding the frequency of the radiation, power of the source, and surrounding environment is essential for anyone working with microwave radiation. Lower frequency waves can travel further but have less energy, while higher power sources produce more intense fields to overcome obstacles and interference. Finally, obstacles and atmospheric conditions can limit the range of microwave radiation.
Power of the Source
Microwave radiation is like an invisible superpower that has revolutionized the way we live. But what determines the strength of this power? As an expert on the “Power of the Source”, I can tell you that the answer lies in understanding the relationship between power and frequency, which are the two key factors that determine how far microwaves can travel.
First, let’s talk about power. The strength of a source of microwave radiation is measured in watts. Higher wattages produce more powerful microwaves that can travel farther. For instance, a 1200-watt microwave oven will produce more powerful microwaves than a 600-watt one, allowing it to travel up to 10 meters (33 feet) before weakening.
However, frequency is also crucial in determining how far microwave radiation can travel. The frequency of microwaves affects their wavelength, and higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths that are more easily absorbed by objects along their path. This means that microwaves with higher frequencies are less effective at traveling long distances than those with lower frequencies.
For example, a typical microwave oven operates at a frequency of 2.45 GHz, which allows it to travel up to 10 meters before weakening. But military and weather radar systems use much higher frequencies and can generate power outputs in the millions of watts, allowing them to travel much farther distances than microwave ovens.
It’s important to note that even though microwave radiation can travel long distances, objects along its path can absorb it quickly, reducing its effective range. Trees, buildings, and other obstacles can cause the energy of microwaves to dissipate quickly, further reducing their range.
Obstacles and Barriers in Its Path
Microwave radiation has revolutionized our world with its incredible power. However, its range can be significantly impacted by obstacles and barriers along its path. As an expert in the field, I can tell you that these obstructions act like Kryptonite to weaken its abilities.
The strength of microwave radiation depends on the power and frequency of the source. Higher wattages produce stronger microwaves that can travel further, while higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths that are absorbed more easily by objects along their path, limiting their range.
The type and density of the material that microwave radiation encounters play a crucial role in determining how far it can travel. Glass, plastic, and most types of ceramics pose no significant barrier to microwave radiation, allowing it to pass through easily. However, metal objects such as aluminum foil, stainless steel containers, and even some metallic paints can reflect or absorb the radiation, preventing it from traveling any further.
Similarly, walls and other building materials made of concrete, brick, or stone can limit the range of microwave radiation. The denser the material, the more energy it absorbs or reflects, reducing the distance that the radiation can travel. In fact, microwave ovens have metal casings and glass doors to prevent the radiation from escaping and potentially causing harm to people or objects outside of the oven.
Even air can act as a barrier to microwave radiation. The higher the frequency of the radiation, the more easily it is absorbed by air molecules. This is why high-frequency microwaves used for satellite communication can only travel short distances through the atmosphere before being absorbed.
Safety Guidelines When Using Microwaves
While microwaves are incredibly convenient appliances, they emit radiation that can be harmful if not used properly. To ensure that you and your loved ones remain safe while using a microwave, it is crucial to follow some basic safety guidelines.
The first thing to keep in mind is that microwaves emit non-ionizing radiation, which means it does not have enough energy to cause damage to DNA. However, high levels of exposure can still be dangerous. So, always stand at least a few feet away from the microwave when it is in use and avoid standing directly in front of it. This will help limit your exposure to any potential radiation leakage.
Proper maintenance of the microwave is also key to ensuring safety. If you notice any cracks or damage to the door or seal of the microwave, stop using it immediately and have it repaired or replaced. Damaged microwaves can leak radiation, which can be harmful to your health.
When cooking or reheating food in the microwave, always use microwave-safe containers. Avoid using plastic containers that are not labeled as microwave-safe as these can potentially melt or release harmful chemicals into your food. Metal containers should also be avoided as they can cause sparks and potentially damage your microwave.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using your microwave to ensure proper usage and avoid overloading the microwave with too much food at once. By following these simple safety guidelines, you can help ensure that your microwave remains a safe and convenient appliance for years to come.
Health Risks Associated with High Levels of Microwave Radiation

Microwaves are a fascinating form of electromagnetic radiation that we encounter every day. From cooking food in microwaves to transmitting information in telecommunications systems, they make our lives easier in countless ways. But what about the potential health risks associated with high levels of microwave radiation?
The most common health risk associated with microwave radiation is thermal damage. When microwaves are absorbed by the body’s tissues, they can cause them to heat up and potentially lead to burns, tissue damage, or even death. This is why it’s crucial to always follow safety guidelines and regulations when using microwaves.
However, it’s not just thermal damage that we need to be concerned about. Some studies suggest that exposure to high levels of microwave radiation may also lead to genetic mutations, cancer, and neurological disorders. While more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of microwave radiation exposure, it’s important to take these potential risks seriously.
Factors such as frequency, intensity, duration of exposure, and individual sensitivity to radiation can all impact the effects of microwave radiation exposure on our health. That’s why it’s crucial to limit exposure where possible and follow safety guidelines at all times.
To stay safe while using microwaves, always keep a safe distance from the appliance while it’s in use and avoid using damaged microwaves or non-microwave-safe containers. By taking these simple precautions, we can protect ourselves from potential health risks associated with high levels of microwave radiation.
6dY8zo1PkoM” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, microwave radiation is a powerful and intriguing form of electromagnetic energy that has revolutionized our world. It’s an integral part of our daily lives, from warming up leftovers to enabling seamless communication through cell phone signals. However, the distance it can travel and its impact on us depend on several factors, including frequency, power of the source, surrounding environment, and obstacles along its path.
Microwave ovens operate at a frequency of approximately 2.45 GHz, which corresponds to a wavelength of about 12 centimeters. This frequency is perfect for heating food because it’s efficiently absorbed by water molecules. However, its range is limited to just a few meters, making it unsuitable for long-distance communication or radar applications.
Microwave communication systems use frequencies between 6 and 60 GHz with wavelengths ranging from 5 to 0.5 centimeters. These frequencies have a larger range than those used in microwave ovens but still face limitations due to atmospheric absorption and the curvature of the Earth’s surface.
Although microwaves are generally safe at low levels, high-level exposure can be harmful. To protect ourselves from potential health risks associated with high levels of microwave radiation exposure, we should follow safety guidelines when using microwave ovens or other sources of microwave radiation. Simple precautions like using microwave-safe containers and avoiding standing too close while in use can go a long way in ensuring our safety.
Overall, understanding how far microwave radiation can travel and its impact on our lives is crucial for anyone working with this energy source.