Microwaves are the unsung heroes of our kitchens, helping us whip up meals in a flash. But have you ever stopped to ponder the inner workings of these nifty appliances? Maybe you’ve even found yourself asking, “How many MHz is the average microwave?”
Well, it turns out that this seemingly simple question has a surprisingly complex answer. Typically, microwaves operate at a frequency of 2.45 GHz (or 2450 MHz). This frequency was chosen because it’s easily absorbed by water molecules – which makes it perfect for cooking food.
But why does this matter? And how exactly does it impact your cooking experience? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the science behind microwave cooking and explore how MHz comes into play. Plus, we’ll take a trip down memory lane and discover how microwaves went from laboratory equipment to must-have kitchen gadgets.
So whether you’re a curious foodie or just want to impress your friends with some newfound knowledge about your microwave, keep reading. We promise to dish out all the juicy details and answer that burning question: just how many MHz is the average microwave?
Contents
What is a Microwave?
Microwave ovens have transformed the way we cook and heat food, becoming an essential appliance in most households today. But what exactly is a microwave?
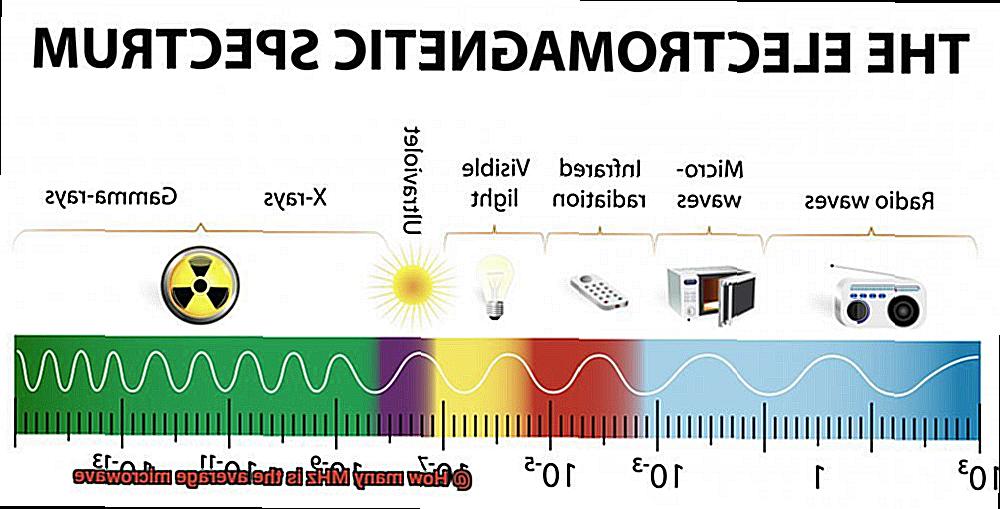
Microwaves are a type of radio waves with a frequency ranging from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. The term “microwave” comes from the fact that these ovens use microwave frequency radiation as their source of heat. The average microwave operates at a frequency of 2450 MHz, equivalent to a wavelength of approximately 12 centimeters. This specific frequency was chosen due to regulations set by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) use.
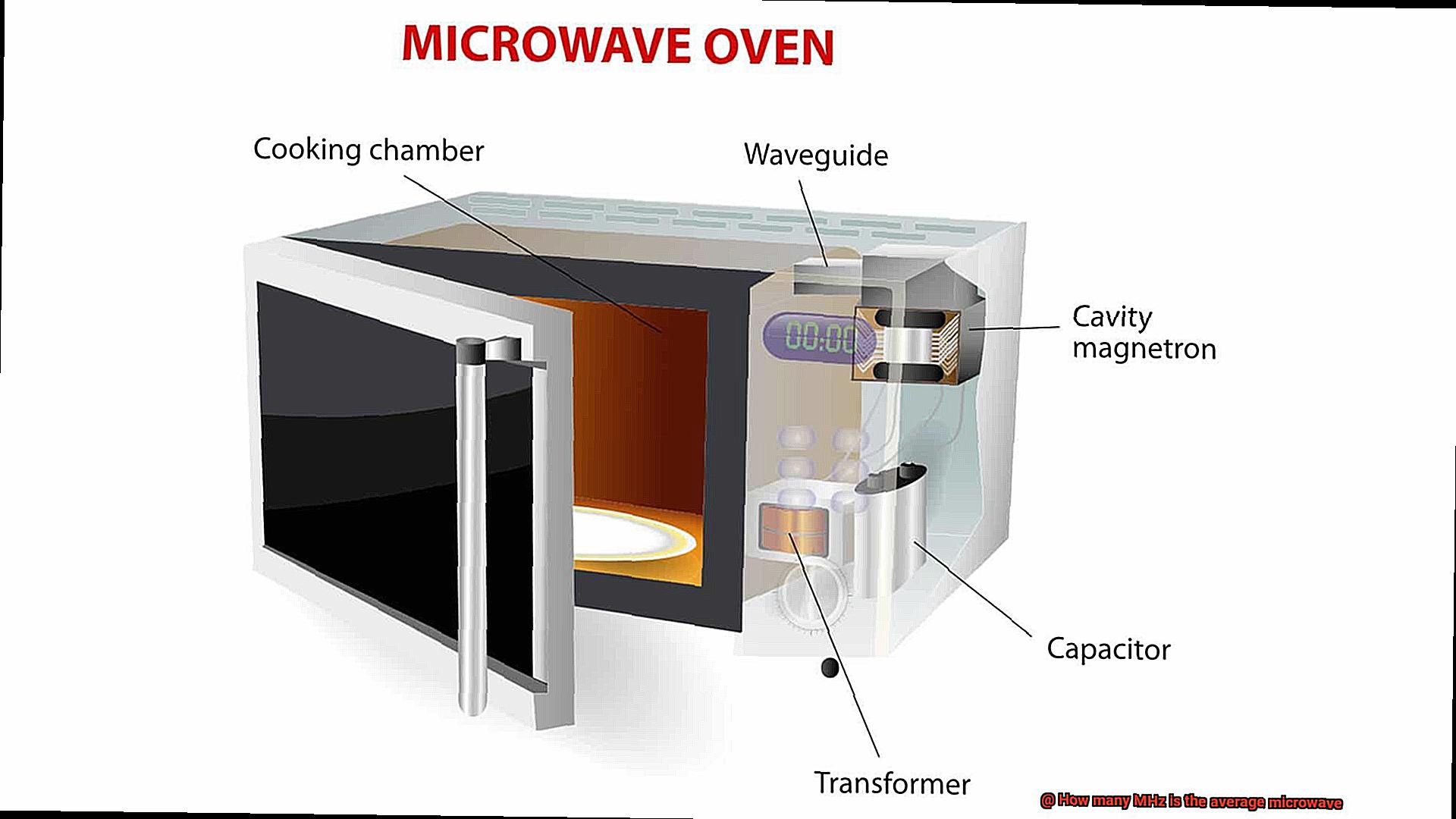
When you place food in a microwave oven and turn it on, the microwaves produced by the oven are absorbed by the food. This absorption causes water molecules in the food to vibrate and generate heat, rapidly heating up your food. Unlike conventional ovens which heat food from the outside in, microwaves heat food from the inside out, making them incredibly efficient.
Microwave ovens were first developed during World War II when researchers discovered that microwaves could be used to heat food quickly. However, it wasn’t until the late 1960s and early 1970s that microwave ovens became popular in households.
Today, there are many different types of microwave ovens available on the market with various features. Some models may operate at slightly higher or lower frequencies, but they are still within the ISM band. However, the difference in frequency between different models does not significantly affect their performance or heating capabilities.

In addition to heating and cooking food, microwave ovens can also be used for other purposes such as sterilizing sponges or heating up hot packs for pain relief. Yet it’s important to note not all materials are safe to be placed in a microwave oven, so it’s crucial to read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
What is MHz?

MHz is an abbreviation for megahertz, and it is a unit of frequency commonly used in electronics and telecommunications. This term refers to the number of cycles per second in a wave or signal. Simply put, it indicates how many times a wave or signal repeats itself in one second.
Now, let’s dive into microwaves. These nifty kitchen appliances use electromagnetic radiation to heat up your food. The frequency range of this radiation is around 300 MHz to 300 GHz, but the specific frequency used by a microwave oven varies depending on its design.
Why does the frequency matter? The size of the waves produced by the microwave oven is determined by its frequency, which affects how well the microwaves are absorbed by the food being heated. If the waves are too large, they won’t heat up your food at all. Conversely, if they’re too small, they’ll be absorbed too quickly and could cause your food to burn.
Most household microwave ovens operate at a frequency of 2.45 GHz because this frequency can penetrate most common materials without causing harm and is easy to generate using electronic circuits. It’s fascinating how something as simple as selecting the right frequency can make such a huge difference in how well your food is heated.
The Average Frequency of a Microwave Oven
Microwave ovens are a kitchen essential, providing quick and effortless food heating and cooking. However, have you ever wondered how these appliances work? One crucial aspect is the frequency at which they operate.
The average frequency of a microwave oven is 2.45 GHz, and this means that it oscillates at an astounding rate of 2.45 billion cycles per second. This frequency has been standardized for household use worldwide, making it easy for manufacturers to produce and consumers to purchase replacement parts.
But why was this specific frequency chosen? Well, this frequency allows microwaves to be absorbed by water molecules, which is what causes food to heat up. Interestingly, this frequency was selected as it’s the most efficient at causing water molecules to vibrate, generating heat and cooking the food from the inside.
Furthermore, the wavelength of 2.45 GHz is small enough to fit within the dimensions of a typical microwave oven, ensuring even cooking throughout your food. So no matter where your dish is placed in the oven, it will receive an equal amount of energy.
It’s worth noting that not all microwaves work at precisely 2.45 GHz. Some may operate at slightly different frequencies such as 2.4 GHz or 2.5 GHz but are still within the acceptable range for household use.
Why Was the 2.45 GHz Frequency Chosen?
It’s not just a random number, but rather a carefully chosen frequency that has revolutionized the way we cook food. As an expert on this topic, let me take you through the fascinating science behind it.
Microwave ovens work by creating an electromagnetic field that oscillates at a specific frequency, causing water molecules in food to vibrate and produce heat. But why 2.45 GHz? Well, it turns out that water molecules absorb the most energy at this frequency, making it the most efficient frequency for cooking food. This means your meal is heated more quickly and evenly than if a different frequency was used.
But that’s not all. The 2.45 GHz frequency was also chosen because it has minimal interference with other electronic devices, such as radios and televisions. This is because it’s not commonly used for other types of devices, making it a safe and reliable choice for microwave ovens. Imagine trying to heat up your dinner while your favorite TV show keeps cutting out – not ideal.
It’s worth noting that the 2.45 GHz frequency has been extensively tested and found to be safe for human usage when used within recommended limits. So you can enjoy your piping hot meal without any health concerns.
Are All Microwaves the Same Frequency?
Well, the answer is no. As an expert in the field, I can tell you that while most household microwaves operate at a frequency of 2.45 GHz, there are variations in frequency among different types of microwaves.
Let’s delve into the reasons why some microwaves operate at different frequencies. Firstly, commercial and industrial microwaves need to operate at higher frequencies, such as 5.8 GHz or 915 MHz, depending on their specific application. For example, in industries such as pharmaceuticals, ceramics, and electronics, precise heating is crucial. These higher frequencies allow for more accurate control over the heating process and are better suited to these industries.
Secondly, some microwaves come with multiple power levels that can adjust the frequency of operation based on the desired heating intensity. This feature is particularly useful when cooking delicate foods that require slow heating or defrosting.
But why does this matter to you? Understanding the frequency of your microwave can help you make informed decisions about cooking times and power settings for optimal results. If your microwave operates at a higher frequency, it may heat food faster, but it may not be suitable for delicate dishes that require slower cooking times. Conversely, if your microwave operates at a lower frequency, it may take longer to heat food but may be more suitable for delicate dishes.
Does the Frequency Affect Performance?
If you’re in the market for a microwave oven, you might be wondering how the frequency of the oven affects its performance. As an expert in this field, I can tell you that the frequency of a microwave oven does indeed play a role in its performance, but it’s not the only factor to consider.
Let’s start by delving into what frequency means in the context of microwave ovens. Microwaves use electromagnetic waves with a frequency range of 2.4 to 2.5 GHz, also known as the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) band. This particular frequency range is utilized because it interacts with food molecules like water, fats, and sugars causing them to vibrate and heat up.
Now, let’s talk about how frequency affects performance. The higher the frequency, the more energy is needed to generate electromagnetic waves. Therefore, a higher frequency oven will cook food faster and more evenly than a lower frequency one. However, there are safety limits to how high the frequency can be before it becomes dangerous for human health. Fortunately, the ISM band used for microwaves is deemed safe since it falls within the non-ionizing radiation range.
It’s important to note that frequency isn’t the sole factor that influences performance. The wattage of the oven and the size and shape of the cooking chamber also contribute significantly to the microwave’s optimal performance. A higher wattage oven will cook food faster than a lower wattage one, while a larger cooking chamber may require more time to heat up and cook food uniformly.
Furthermore, microwave ovens are designed to operate at specific frequency ranges. Changing the frequency can potentially damage or even cause them to malfunction. Therefore when shopping for a microwave oven, it’s essential to examine all of its features and specifications, not just focus on frequency alone. Consider various factors such as wattage, cooking chamber size and shape, and additional features such as convection or defrosting options.
-e9Ssrzn9tk” >
Conclusion
In summary, the average microwave operates at a frequency of 2.45 GHz or 2450 MHz, a carefully chosen frequency that is absorbed effortlessly by water molecules making it ideal for cooking food. By creating an electromagnetic field that oscillates at this specific frequency, microwave ovens cause water molecules in food to vibrate and produce heat, resulting in deliciously cooked meals.
It’s worth noting that while most household microwaves operate at 2.45 GHz, there are variations in frequency among different types of microwaves. Commercial and industrial microwaves require higher frequencies based on their specific application. Additionally, some microwaves come with multiple power levels that can adjust the frequency of operation based on the desired heating intensity.
Frequency alone doesn’t dictate optimal performance when it comes to microwave ovens; other factors such as wattage and cooking chamber size and shape also play significant roles. Therefore, when shopping for a microwave oven, it’s crucial to examine all its features and specifications thoroughly. Consider additional features such as convection or defrosting options alongside the wattage and cooking chamber size and shape.
Understanding the frequency of your microwave oven can help you make informed decisions about cooking times and power settings for optimal results.






