Have you ever marveled at the magic of microwaves in your kitchen? These incredible devices have transformed the way we cook and warm our food, and they continue to amaze us with their efficiency. But have you ever stopped to ponder the science behind it all? Microwaves are electromagnetic waves that heat up our food, and different frequencies come into play. So, what is the best microwave frequency?
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the fascinating world of microwaves and explore the ideal microwave frequencies. We’ll take a closer look at what microwaves are, how they work, and how varying frequencies impact their performance. Additionally, we’ll explore how microwave frequencies affect aspects like food quality, safety, and health. Plus, we’ll examine the various types of microwaves available today and explain why choosing the correct frequency is crucial for getting optimal results from your microwave.
Whether you’re a curious science enthusiast or looking to upgrade your kitchen appliances, this article has everything you need to know about finding the perfect microwave frequency. So get ready for an exciting journey into the world of microwaves – where science meets culinary magic.
Contents
What is Microwave Frequency?
Microwave frequency is a fascinating aspect of modern technology that plays a crucial role in various applications. It refers to the frequency range of electromagnetic waves that oscillate rapidly, typically between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Let’s dive deeper into the world of microwave frequency and explore its importance in different fields.
Firstly, microwave ovens rely heavily on frequency to heat food quickly and efficiently. The 2.45 GHz frequency is the standard for household microwave ovens as it is highly absorbed by water molecules, making it ideal for heating food. Meanwhile, industrial microwave ovens use the 915 MHz frequency, which has a longer wavelength that penetrates thicker materials better. For example, it’s commonly used in the food industry for drying and sterilizing processes.
The selection of the appropriate microwave frequency depends on several factors, including the material being heated or processed. The material’s dielectric properties must be considered when choosing a frequency range that provides optimal performance. Some materials may require specific frequencies for optimal heating while others may be damaged at high frequencies.
Microwave frequencies are not only used in ovens but also in communication systems, radar technology, and medical imaging. High-frequency microwaves are suitable for short-range communication systems while low-frequency microwaves are better suited for long-range communication systems.
Commonly Used Frequencies in Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens are a staple in most kitchens, but few people know how the magic happens behind the closed door. The secret lies in the frequency of the electromagnetic waves that are emitted by the oven and absorbed by the food, causing molecules to vibrate and generate heat. The frequency used affects how much energy is absorbed, impacting cooking time and efficiency.
The two most commonly used frequencies in microwave ovens are 2.45 GHz and 915 MHz. The 2.45 GHz frequency is ideal for heating up foods with high water content, such as vegetables, meat, and pasta. It’s a resonant frequency of water molecules, meaning it can efficiently transfer energy and generate heat. This frequency is also great at penetrating thick layers of food, ensuring even cooking from all sides.
On the other hand, the 915 MHz frequency is better suited for heating denser materials like rubber, plastic, or wood. Its longer wavelength and lower energy make it less effective at heating water molecules but more efficient at heating dense objects.
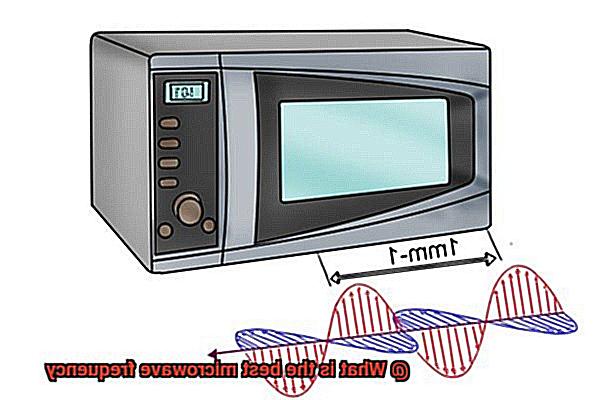
While these two frequencies dominate the market, there are other frequencies that can be used in microwave ovens as well. Commercial models can reach frequencies as high as 5.8 GHz for faster cooking times and higher power output but come with a higher price tag.
So how do you choose which frequency is right for your needs? For most household applications, the 2.45 GHz frequency is ideal due to its ability to efficiently heat water molecules. However, industrial applications may require other frequencies depending on the materials being heated.
Advantages of 2.45 GHz Frequency

Its versatility, affordability, and accessibility make it a popular choice for various applications, including wireless communication, remote sensing, and indoor networking.
Perhaps one of the most significant advantages of this frequency is that it is globally unlicensed. This means that it can be used without a license in most countries, making it an affordable and accessible option for many applications. No need to worry about costly licensing fees or restrictions on usage.

Another key benefit of the 2.45 GHz frequency is its low atmospheric attenuation. This feature allows signals to travel long distances without significant signal loss, making it ideal for applications such as wireless communication and remote sensing. Whether you’re sending data wirelessly or collecting information from a remote location, the 2.45 GHz frequency is a reliable option.
In addition to its long-range capabilities, the 2.45 GHz frequency has excellent penetration abilities. It can penetrate walls and other obstacles with ease, making it suitable for indoor applications such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth communication. So whether you’re streaming movies on your laptop or sending files to a colleague across the room, this frequency has got you covered.
Moreover, the 2.45 GHz frequency requires relatively low power compared to other frequencies. This makes it energy-efficient and an excellent option for applications that require low power requirements. You can enjoy reliable connectivity without worrying about high energy bills or battery drainage.
Last but not least, the 2.45 GHz frequency has low interference with other radio frequencies. This means that it can be used in environments with multiple devices without causing any interference issues. You won’t have to worry about your signal getting lost in a sea of other wireless transmissions.
Advantages of 915 MHz Frequency
Wireless communication has revolutionized the way we connect with each other and conduct business. As technology advances, so does the need for more efficient and effective communication tools. Enter the 915 MHz frequency – a remarkable microwave frequency that offers several advantages for wireless communication and industrial applications.
One of the most significant advantages of the 915 MHz frequency is its ability to penetrate through objects such as walls, making it an excellent choice for indoor wireless communication. This frequency’s longer wavelength enables it to pass through obstacles more easily than higher frequencies, making it a perfect option for communication within buildings or other structures.
Another advantage of this frequency is its lower atmospheric attenuation compared to higher frequencies. This feature means that the signal can travel longer distances without losing strength, making it ideal for long-range wireless communication applications. Additionally, the signal is less affected by weather conditions, which can cause interference and reduce signal strength.
Moreover, the 915 MHz frequency has a high absorption rate in water and other materials, making it highly effective in industrial applications such as heating and drying processes. It’s also used in RFID technology for asset tracking and identification, as well as medical devices such as blood glucose monitors.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Suitable Microwave Frequency
Microwaves have become an indispensable part of our daily lives, making our food preparation quick and easy. However, the frequency of the microwave plays a crucial role in its performance. As an expert in this field, I can tell you that selecting the right frequency for your intended use is essential to getting the most out of your microwave.
One of the primary factors to consider when selecting a suitable microwave frequency is the size of the object being heated. Larger objects require lower frequencies, while smaller objects require higher frequencies. A lower frequency penetrates deeper into larger objects and heats them evenly, while a higher frequency is absorbed more quickly and is better for heating smaller objects.
Another crucial factor to consider is the material of the object being heated. Different materials absorb microwave energy differently, which can affect the performance of the microwave. For example, water and fats absorb microwaves more readily than other materials, so if you’re heating food that contains a lot of water or fat, a lower frequency may be more effective.
The power output of the microwave is also an essential consideration when selecting a suitable frequency. Higher frequencies require higher power levels to achieve the same level of heating as lower frequencies. Therefore, if you need to heat something quickly or if you have a large item that requires a lot of energy, a lower frequency may be more suitable.
Finally, it’s vital to consider any interference from other devices when selecting a suitable microwave frequency. Microwaves operate on similar frequencies to other wireless devices such as Wi-Fi routers and Bluetooth devices. If there are other devices operating on the same frequency in the same area, it can cause interference and affect the performance of your microwave. In such cases, it may be necessary to select a different frequency or adjust the power output to minimize interference.
Dielectric Properties and Their Impact on Microwave Frequency
The science behind microwave frequency is a fascinating topic that revolves around the dielectric properties of materials. Dielectric materials are non-conductors that can store energy in an electric field. When exposed to an electromagnetic wave, such as a microwave, these materials can absorb energy based on their dielectric constant or relative permittivity. This property plays a crucial role in determining the best microwave frequency for a particular application.
Here are some things to explore:
- Microwave Ovens: Have you ever wondered why your leftover pizza heats up so quickly in the microwave? The answer lies in the dielectric properties of water molecules, which are the primary absorbers of microwaves in food. The frequency of 2.45 GHz used in microwave ovens corresponds to a resonance of water molecules, making it the most efficient frequency for heating food.
- Radar Systems: Did you know that different types of materials require different microwave frequencies to be detected? Metallic objects reflect microwaves well, making them detectable with high-frequency microwaves (e.g., 10-100 GHz). However, non-metallic objects have lower dielectric constants and absorb less energy at higher frequencies, so they require a lower frequency (e.g., 1-5 GHz) to be detected.
Understanding the dielectric properties of materials is crucial for selecting the best microwave frequency for a particular application. By taking these factors into account, one can achieve the desired outcome more efficiently. Without this understanding, you may end up with a soggy sandwich or a missed object on your radar system.
_IRAi6Nzxbk” >
Conclusion
To sum it up, determining the best microwave frequency is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It depends on various factors like the material you are heating or processing, the size of the object, and the power output of your microwave. Microwave ovens use different frequencies to heat food quickly and efficiently.
For household microwaves, the 2.45 GHz frequency is perfect as it is highly absorbed by water molecules, making it ideal for heating foods with high water content. On the other hand, industrial microwaves use the 915 MHz frequency, which has a longer wavelength that penetrates thicker materials better.
The dielectric properties of materials play an important role in determining the ideal microwave frequency for a particular application. Different types of materials require different microwave frequencies to be detected or heated efficiently.
Apart from cooking food, microwave frequencies are also used in communication systems, radar technology, and medical imaging. High-frequency microwaves work well for short-range communication systems while low-frequency microwaves are more suitable for long-range communication systems.
Knowing these factors is crucial when selecting the best microwave frequency for your intended use.