Do you ever stop to think about the science behind your microwave oven? It’s not just a magical box that turns cold leftovers into steaming hot meals. No, it uses a type of energy called microwaves that have a unique ability to make molecules vibrate, heating up your food from the inside out. But have you ever wondered about the wavelength of those microwaves?
The wavelength of a microwave oven is actually quite small – around 12.2 cm, much smaller than radio waves or light waves. And that wavelength plays a crucial role in how well your food cooks in the oven. Understanding this concept can help you optimize your cooking times and avoid undercooked or overcooked meals.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the physics of microwave ovens and explore the concept of wavelength in detail. We’ll discuss how microwaves work, why their wavelength matters for cooking, and even some interesting facts about how they’re used in modern technology. So whether you’re a seasoned chef or just someone who loves their microwave popcorn, get ready to learn all about the fascinating world of microwave ovens.
Contents
What is the Wavelength of a Microwave Oven?
Microwave ovens have revolutionized the way we cook and heat our food. But have you ever wondered about the science behind this appliance? One crucial aspect of a microwave oven is its wavelength, which determines how effectively it interacts with the food being cooked.
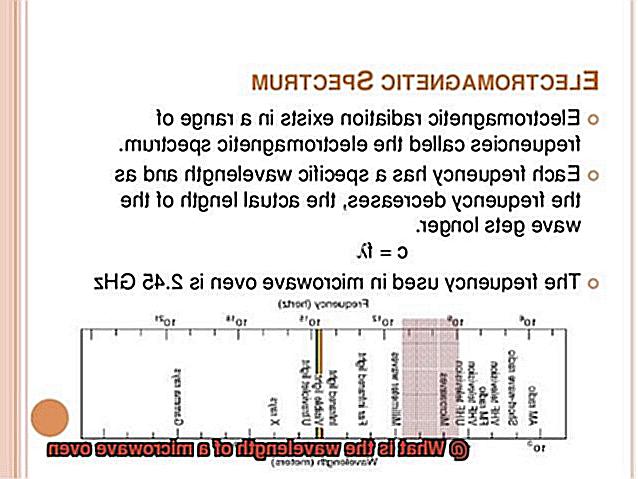
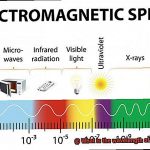
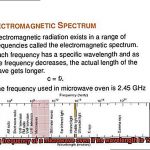
The wavelength of a microwave oven is the distance between two peaks of the electromagnetic wave it emits. Typically, it ranges from 1 millimeter to 1 meter, with a frequency of 300 MHz to 300 GHz. The most commonly used frequency for microwave ovens is 2.45 GHz, which corresponds to a wavelength of approximately 12.2 centimeters.
Understanding the wavelength of a microwave oven is important because it determines how the microwaves interact with the food. These waves are absorbed by water, fats, and sugars in the food, causing them to vibrate rapidly and generate heat. The size of the wavelength determines the size of the areas within the oven that can be heated effectively. If the wavelength is too large, certain areas of the food may not be heated evenly.
The frequency of microwaves is also measured in Hertz (Hz), which is the number of cycles per second that the wave completes. The frequency of a microwave oven typically ranges from 2.45 GHz to 5.8 GHz, with higher frequencies corresponding to shorter wavelengths.
It’s important to note that the wavelength of a microwave oven can also affect how it interacts with other objects. For example, if the wavelength matches the size of an object, it can absorb or reflect the microwaves, causing interference or distortion in the signal. This is why metal objects should be kept out of a microwave oven.
In addition to cooking food, microwaves are utilized in various applications such as telecommunications, medical imaging, and radar. In these applications, engineers carefully control the wavelength and frequency of microwaves to achieve specific results.
How Does the Wavelength of a Microwave Affect Food?
Microwave ovens have become a staple in modern kitchens, providing a quick and efficient way to cook food. But have you ever considered how the wavelength of a microwave affects your food? As an expert in this field, I am here to provide you with fascinating insights.
Firstly, let’s delve into what wavelength means. It refers to the distance between two peaks of an electromagnetic wave. The wavelength of a microwave oven is typically around 12.2 centimeters, which is much longer than the wavelengths of visible light measured in nanometers.
Now, let’s explore how the wavelength affects your food. When microwaves enter food, they cause water molecules to vibrate rapidly and generate heat. The longer the wavelength of the microwave, the deeper it can penetrate into the food. This means that microwaves with longer wavelengths can heat thicker foods more evenly than those with shorter wavelengths.
Furthermore, different foods absorb microwave energy differently depending on their chemical composition and structure. For instance, fatty foods absorb microwaves more readily than watery foods because they contain more polar molecules that can interact with the microwaves.
But what about the texture and quality of the food after cooking? Studies have suggested that long-term exposure to microwaves can alter the structure of proteins and other molecules in food, potentially affecting its nutritional value and taste. Hence, it’s essential to use your microwave judiciously.
What is the Frequency of a Microwave Oven?
First, let’s talk about frequency. It refers to the number of cycles per second that a wave completes. The frequency of a microwave oven is typically around 2.45 gigahertz (GHz), which means that the waves oscillate at a rate of 2.45 billion cycles per second. While this may sound like a lot compared to other household appliances, it’s actually much lower than the frequencies of visible light, which range from around 400 to 800 terahertz (THz), or trillions of cycles per second.
So why do microwave ovens use this particular frequency? The answer lies in how microwaves interact with food. Microwaves are a type of radio wave with a high frequency and short wavelength. They’re absorbed by water molecules, fats, and sugars in food. When these molecules absorb the microwaves, they start to vibrate rapidly, generating heat and cooking the food from the inside out.
This is why thicker foods take longer to cook in a microwave than thinner foods – the microwaves have to penetrate deeper into the food to heat up all those water molecules. And this is also why you should be careful when reheating liquids in a microwave – if they get too hot, they can boil over.
It’s worth noting that different countries may use slightly different frequencies for their microwave ovens. For example, some countries in the European Union use a frequency of 2.5 GHz instead of 2.45 GHz. However, these differences are relatively minor and don’t really affect how the microwave oven functions.
How Does the Wavelength of a Microwave Affect Other Objects in its Environment?
It’s important to note that microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves with a wavelength range of one millimeter to one meter. These radio waves cause food molecules to vibrate rapidly, generating heat and cooking the food. But what about other objects in the microwave’s vicinity?
First and foremost, metal objects can reflect microwaves instead of absorbing them like food does. This reflection can cause sparks or even damage to the oven itself, so it’s best to avoid putting metal in your microwave altogether.
But that’s not all – the thickness and density of an object placed in the microwave can also impact its heating process. Thicker and denser objects may not absorb microwaves as effectively as thinner and less dense ones, leading to uneven heating and cold spots within the food. So if you’re looking for an evenly heated meal, opt for thinner and less dense items.
Lastly, where you place your food within the microwave can also affect its heating. Placing it in the center of the turntable ensures even exposure to the microwaves, while placing it off-center can result in uneven heating and unsatisfactory results.
Understanding the Wavelength of a Microwave Oven for Cooking Purposes
These magical machines have become a staple in most kitchens, making cooking and reheating meals a breeze. But have you ever wondered how they work? Specifically, how does the wavelength of a microwave oven affect the cooking process? Fear not, my culinary friends, for I am here to shed some light on this topic and help you achieve perfect cooking results every time.
Let’s start by defining wavelength. In simple terms, it’s the distance between two peaks of a wave. When it comes to microwaves, the wavelength is typically measured in millimeters or centimeters. Depending on the model and manufacturer, the wavelength of a microwave oven can range from 12 cm to 30 cm.
But why is this important for cooking purposes? Well, the wavelength determines how well the microwaves penetrate and heat food. Microwaves with shorter wavelengths are more powerful and can penetrate deeper into food. This makes them ideal for cooking larger or denser items like roasts or casseroles that require even heating throughout. On the other hand, microwaves with longer wavelengths are less powerful and work best for heating smaller or thinner items like soup or leftovers.
However, it’s worth noting that different parts of the food will absorb microwaves differently based on their composition and density. For example, water molecules are excellent at absorbing microwave energy. This is why most microwave-safe containers are made of glass or ceramic since these materials don’t absorb microwaves as much as plastic or metal.
Now that we understand how wavelength affects cooking, let’s explore some practical tips:
- Choose a microwave with a shorter wavelength (around 12-15 cm) for larger or denser items like meats or casseroles.
- Opt for a microwave with a longer wavelength (around 25-30 cm) for smaller or thinner items like soup or leftovers.
- Use microwave-safe containers made of glass or ceramic to ensure proper heating without any unwanted sparks or damage.
- Remember to stir or rotate your food halfway through the cooking process to ensure even heating.
Understanding the Wavelength of a Microwave Oven for Safety Purposes
Microwave ovens have revolutionized the way we cook and reheat food, but they are not without their risks. As an expert in this field, I am here to share with you why understanding the wavelength of a microwave oven is critical for safety purposes.
The wavelength of a microwave oven refers to the distance between two peaks of an electromagnetic wave. The wavelength of a microwave oven is approximately 12 centimeters or 4.7 inches, with a frequency of around 2.45 gigahertz. This information is essential because when microwaves are absorbed by food, they create thermal energy that heats up the food. However, these same waves can also create thermal energy when absorbed by the human body, leading to burns and tissue damage.
To ensure safety while using a microwave oven, there are several things you need to keep in mind. First and foremost, use only microwave-safe containers made of glass or ceramic. Avoid using metal or aluminum foil as these can reflect microwaves and cause sparks that can be dangerous. Furthermore, always keep the door of the microwave oven closed during operation as it has a special mesh that prevents microwaves from escaping while allowing you to see inside.
Tips on Using Your Microwave More Effectively
Microwaves are a popular kitchen appliance that most of us use on a daily basis. However, are you using your microwave to its full potential? Here are some tips and tricks to help you use your microwave more effectively:
Use Microwave-Safe Containers
Using the wrong containers in your microwave can lead to harmful chemicals being released or even cause fires. It’s crucial to use microwave-safe containers that are labeled as such. Avoid metal containers or containers with metal trimmings, and opt for glass, ceramic, or plastic containers instead.
Cover Your Food
Covering your food while microwaving helps to trap moisture and heat, resulting in faster and more even cooking. Use a microwave-safe cover or a damp paper towel to cover your food, and avoid using plastic wrap or aluminum foil.
Stir or Rotate Your Food
Microwaves cook from the outside in, so it’s important to stir or rotate your food halfway through cooking to ensure that it’s evenly cooked. This is especially important for foods like soups, stews, or casseroles.
Use the Right Power Level
Most microwaves have different power levels that can be adjusted depending on what you’re cooking. Using the right power level can prevent overcooking or drying out your food. For example, use a lower power level when reheating leftovers or cooking rice, and use a higher power level for quick-cooking foods like vegetables.
Don’t Overcrowd Your Microwave
Overcrowding your microwave can result in uneven cooking, which can lead to some parts of your food being undercooked while others are overcooked. Make sure there is enough space between items for the microwaves to circulate properly. If you need to cook a large amount of food, consider cooking it in batches.
Experiment with Different Cooking Techniques
Your microwave is capable of more than just reheating leftovers. Experiment with different cooking techniques like steaming vegetables, poaching eggs, or even making popcorn. Just remember to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use caution when handling hot dishes or liquids.
Common Hazards to Avoid When Using Your Microwave Oven
Microwave ovens have become a staple in most modern kitchens, providing us with unparalleled convenience and ease when it comes to cooking food. However, it’s important to remember that these appliances can pose hazards if not used properly. To keep yourself and your home safe, take note of the following common hazards to avoid when using your microwave oven.
The first hazard on our list is overheating. Overheating occurs when food is heated for too long or at too high of a power level, potentially leading to a fire. Always follow the recommended cooking times and power levels provided in your microwave’s manual to avoid this hazard.
Next up are burns. The steam released from heated food can be scorching hot and cause burns if it comes into contact with your skin. Make sure to use oven mitts or a towel when handling hot dishes and allow the food to cool before eating.
Another hazard that you should be aware of is exploding containers. Using certain materials such as aluminum foil or metal containers in a microwave can cause sparks and even start fires. Only use containers that are labeled as microwave-safe to avoid this risk.
Finally, while radiation exposure from a microwave oven is generally not a concern, it’s still important to use caution. Standing too close to the microwave while it’s in operation can expose you to small amounts of radiation, so maintain a safe distance of at least an arm’s length away from the appliance.
To recap, here are the four common hazards to avoid when using your microwave oven:
- Overheating
- Burns
- Exploding containers
- Radiation exposure
Ndp8r0jLNr8″ >
Conclusion
In conclusion, the wavelength of a microwave oven is not just a technical detail, but a fundamental aspect of how your food gets cooked. At 12.2 cm and 2.45 GHz, microwaves are like tiny dancers that make food molecules vibrate and generate heat from the inside out. This knowledge is key to achieving perfect cooking times and avoiding culinary disasters.
The wavelength size determines which parts of your food will get heated more effectively. Longer wavelengths are like superheroes that can penetrate deeper into dense foods such as roasts or casseroles, ensuring even heating throughout. Shorter wavelengths are more like sprinters that work best for smaller or thinner items like soup or leftovers.
But wait, there’s more. The composition and density of different foods also play a role in how they react to microwaves. Water molecules love to absorb microwave energy, while fatty foods are more prone to interacting with microwaves due to their polar molecules.
While microwave ovens have revolutionized modern cooking by saving us time and effort, they come with some risks if not used properly. Overheating, burns, exploding containers, and radiation exposure are all hazards that require caution and awareness.