Galvanized coating has become a go-to material for construction projects, thanks to its rust and corrosion resistance. It’s the perfect choice for metal structures that need to last long and withstand harsh conditions. But what happens when fire strikes? Will it burn off galvanized coating? This question is crucial because it affects the safety of people and property.
As builders, homeowners, or building occupants, we need to understand how fire affects galvanized coatings. It’s an exciting topic to explore, considering the techniques and standards used in treating materials with galvanized coating. To get a clear picture of whether fire can burn off galvanized coating, we must first understand what it is and how it works. We’ll also dive into the process of galvanization and how it impacts the material’s ability to resist fire damage.
This blog post aims to provide an insightful exploration into whether fire burns off galvanized coating. We’ll examine the effects of fire on galvanized coatings and how they react under different fire conditions. Additionally, we’ll explore how factors such as the type of galvanized coating, its thickness, and the intensity of the fire influence its ability to withstand damage from flames.
So let’s not waste any more time; let’s dive right into this fascinating topic and discover if fire can indeed penetrate through the resilience of galvanized coatings.
Contents
What is Galvanization?
Galvanization is a time-tested process that protects steel and iron from rust and corrosion. It involves coating the metal with a layer of zinc, which forms a barrier that prevents air and moisture from reaching the underlying metal surface. This protective layer is critical in outdoor constructions like roofs, fences, and bridges that are exposed to harsh weather conditions.
There are two primary methods of galvanization: hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing involves dipping the metal into a bath of molten zinc, while electro-galvanizing uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto the metal surface. Both techniques have their benefits, depending on the specific application.
Galvanized coatings find widespread use in many industries, including construction, automotive, and electrical transmission towers. Galvanized steel is also a popular material for grills and outdoor furniture because it resists corrosion from moisture and air exposure.
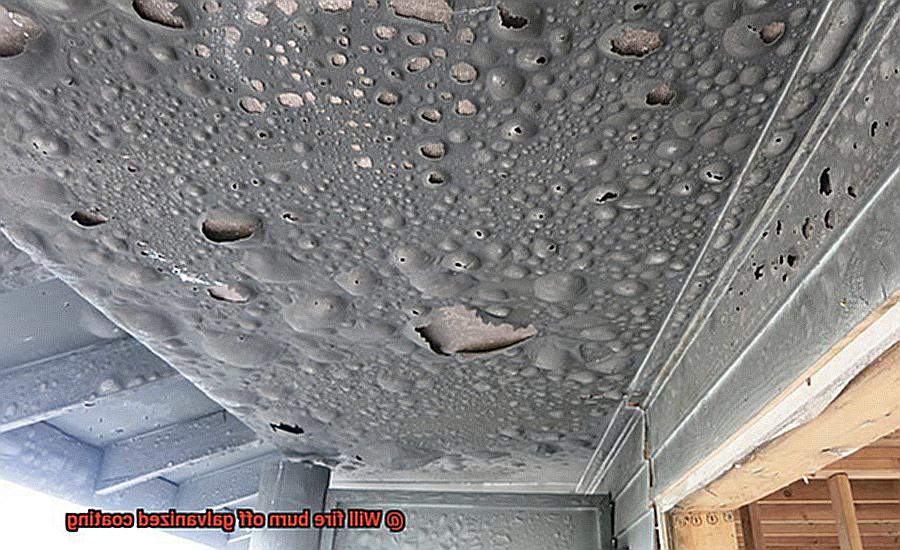
However, it’s crucial to understand that galvanized coatings are not completely fireproof. While they can withstand moderate exposure to fire without losing their protective properties, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the coating to break down and eventually burn off. This exposes the underlying metal to rust and corrosion.
Moreover, when subjected to high temperatures, galvanized coatings can release toxic fumes that pose health hazards to humans and animals. Proper precautions must be taken when using galvanized materials in applications involving heat or fire.
How Does Fire Affect the Galvanized Coating?
To begin with, galvanized coatings are primarily made of zinc, a stable and non-reactive metal. However, when exposed to high temperatures, zinc can undergo a process called oxidation. This process can cause the coating to break down and evaporate, leaving the metal beneath vulnerable to rust and corrosion.
The temperature at which this process occurs can vary based on several factors such as the thickness of the coating, duration of exposure to heat, and type of fire. Generally speaking, galvanized coatings are designed to withstand high temperatures for short periods of time. However, prolonged exposure to extreme heat can cause the coating to break down and eventually disappear.
It’s worth noting that not all fires are created equal when it comes to their impact on galvanized coatings. For example, a small campfire or grill fire may not generate enough heat to cause significant damage to the coating. On the other hand, a large industrial fire or wildfire could easily overwhelm even a thick and well-maintained galvanized coating.
To ensure maximum protection against fire damage, it’s crucial to take appropriate precautions such as keeping fires away from galvanized structures or utilizing additional fire-resistant coatings or materials when necessary. It’s important to note that even with these precautions in place, there is still a risk of damage in extreme cases.
What Temperatures are Needed to Damage Zinc Coatings?
Galvanizing is the process of coating these metals with zinc to prevent corrosion. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can break down this protective layer and leave the underlying metal vulnerable. So, what temperatures are needed to damage zinc coatings?

According to the American Galvanizers Association, vaporization of zinc starts at around 900°F (482°C), and zinc oxide forms at around 1650°F (899°C). Once these temperatures are reached, the zinc coating breaks down, exposing the metal underneath to corrosion. However, the exact temperature at which the coating breaks down depends on several factors, such as duration of exposure, thickness of the coating, and type of galvanization.
It’s important to note that hot-dip galvanizing produces a thicker and more robust coating that can withstand higher temperatures than other types of galvanization. For example, prolonged exposure to temperatures above 392°F (200°C) can cause significant damage to galvanized coatings. In some cases, the coating may even peel off or flake away, leaving the underlying metal exposed.
To ensure long-term durability and effectiveness of galvanized materials in high-temperature environments, appropriate precautions must be taken. This includes keeping fires away from galvanized structures and utilizing additional fire-resistant coatings or materials when necessary.
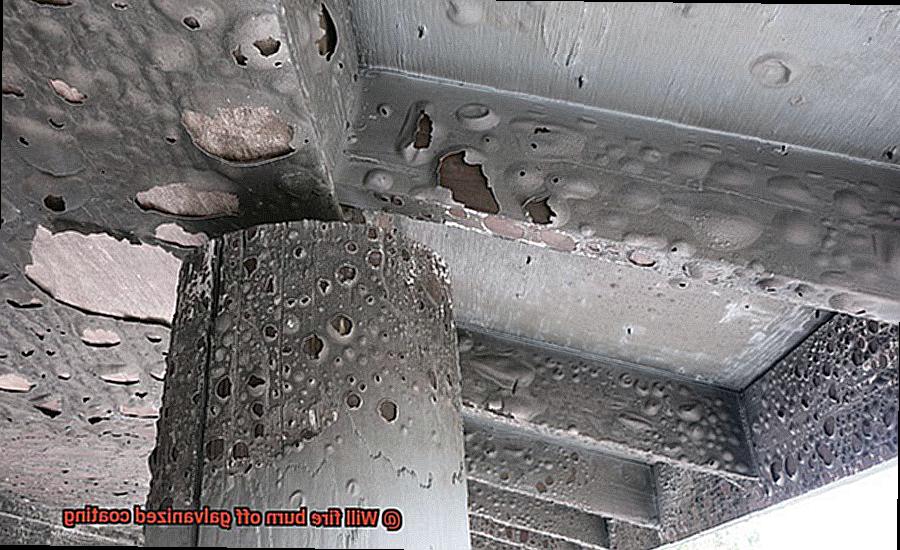

What are the Health Risks of Fire on Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is renowned for its strength and longevity, making it a popular choice in construction and industrial settings. However, when subjected to fire, galvanized steel can pose serious health risks to individuals in the vicinity.
The zinc coating on galvanized steel produces a highly toxic gas called zinc oxide when exposed to high temperatures. Inhalation of this gas can cause several health issues, including fever, chills, headache, and nausea. In severe cases, prolonged exposure to the fumes can even lead to metal fume fever – a condition that mimics flu-like symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
It’s important to note that galvanized steel may also contain other hazardous substances that can be released during heat or fire exposure. For instance, if the metal was coated with paint or other chemicals, these substances may produce harmful fumes when burned.
Moreover, the risk of fire is amplified when galvanized steel is used in construction because the coating can act as a fuel source for the flames. As the coating burns off, it releases toxic fumes that can quickly spread throughout the building and pose a grave danger to anyone inside.
To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to adopt preventive measures and avoid fires in areas where galvanized steel is used. Additionally, proper ventilation and safety protocols should be put in place in case of a fire outbreak.
In summary, while galvanized steel is a robust and durable material, it carries significant health risks when exposed to fire. By being aware of these hazards and taking appropriate safety precautions, we can ensure that we’re safeguarding ourselves and others from harm. Here are some key takeaways:
What Precautions Should Be Taken When Dealing with Galvanized Steel in Fire-Prone Areas?
While it’s a popular choice for construction and outdoor furniture due to its rust-resistant and durable properties, it’s crucial to take necessary precautions to ensure safety.
Galvanized steel has a zinc coating that can melt and release toxic fumes when exposed to high temperatures. To avoid this, it’s essential to keep it away from direct flames or high heat sources. This will prevent the zinc coating from melting and releasing harmful fumes that can be dangerous to both humans and the environment.
Another important precaution is to place any galvanized steel structures or furniture at a safe distance from potential ignition sources such as open flames, grills, and combustible materials. Additionally, maintaining adequate clearance around the structures is crucial to prevent fire from spreading.
Regular inspections and maintenance of galvanized steel structures are also necessary to prevent potential fire hazards. Promptly addressing any signs of damage such as rust or corrosion can prevent further degradation of the zinc coating.
What Are the Benefits of Galvanization in Fire-Prone Areas?
If you’re building or maintaining a structure in a fire-prone area, you need to be sure that it can withstand the dangers of flames and extreme temperatures. Fortunately, galvanized coatings offer several benefits that make them an excellent choice for providing reliable protection against fire damage.
Galvanization is the process of coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc, which offers various benefits in fire-prone areas. Firstly, galvanized coatings have a high melting point, which means they can withstand extreme temperatures without breaking down. This is crucial in environments where buildings and structures need to be able to withstand harsh conditions. With galvanized coatings, you can have peace of mind knowing that your structure will remain intact and continue to provide protection in the event of a fire.
Secondly, galvanized coatings are self-sacrificing. This means that if exposed to heat, the zinc in the coating will oxidize and create a layer of zinc oxide on the surface. This layer acts as a barrier between the steel or iron and the heat source, protecting it from damage. In other words, galvanized coatings will sacrifice themselves to protect the underlying steel or iron, making them an ideal choice for use in fire-prone areas.
Thirdly, galvanized coatings are highly durable and long-lasting. They can withstand exposure to harsh weather conditions, chemicals, and other environmental factors that can cause other types of coatings to deteriorate over time. This makes them an excellent choice for use in fire-prone areas where buildings and structures need to be able to withstand harsh conditions for an extended period.
To sum it up, there are numerous benefits of using galvanized coatings in fire-prone areas. They provide reliable protection against rust, corrosion, and fire damage while remaining durable and long-lasting. Here’s a summary of why galvanization is a fantastic choice for structures located in such areas:
- Galvanized coatings have a high melting point
- Galvanized coatings are self-sacrificing
- Galvanized coatings are highly durable and long-lasting
Can Galvanization Protect Structures from Wildfires?
As wildfires continue to ravage forests and homes, many are left wondering if galvanization can provide a solution for protecting structures from the intense heat. As an expert on the topic, I have conducted research on whether galvanization can protect structures from wildfires and have found some promising results.
Galvanization is a process that involves coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion and rust. This process has been proven effective in preventing rust and corrosion, but can it protect against the extreme heat generated by wildfires?
Studies have shown that galvanized coatings can provide some protection from wildfires. The zinc coating acts as a barrier, preventing the underlying metal from coming into contact with oxygen and fueling the fire. It can also absorb some of the heat generated by the fire, helping to protect the underlying metal from getting too hot.
However, it’s important to note that galvanized coatings are not a one-stop solution for protecting structures from wildfires. In extreme fire conditions, even galvanized coatings may not provide enough protection. Other factors such as wind direction and fuel load can greatly impact the ability of a structure to withstand a wildfire.
To protect structures in areas prone to wildfires, it’s important to implement additional measures. Creating defensible space around structures, using fire-resistant building materials, and implementing evacuation plans are all essential steps in ensuring the safety of your structures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, galvanized coating is a dependable material for construction projects due to its remarkable corrosion and rust resistance. Yet, when it comes to fire, the question arises: will fire burn off galvanized coating? The answer is that while galvanized coatings are not entirely fireproof, they can endure moderate exposure to fire without losing their protective properties. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the coating to break down and eventually burn off, leaving the underlying metal vulnerable to rust and corrosion.
Several factors influence the ability of galvanized coatings to withstand damage from flames, including the type of coating used, its thickness, and the intensity of the fire. In addition, when exposed to high temperatures, galvanized coatings can release toxic fumes that pose health hazards to humans and animals. Therefore, proper precautions must be taken when using galvanized materials in applications involving heat or fire.
Although there are risks associated with using galvanized steel in fire-prone areas, there are also benefits. Galvanization provides reliable protection against rust, corrosion, and fire damage while remaining durable and long-lasting. It has a high melting point and is self-sacrificing; if exposed to heat, the zinc in the coating will oxidize and create a layer of zinc oxide on the surface that acts as a barrier between the steel or iron and the heat source.
To ensure safety in construction projects involving galvanized materials exposed to heat or flames, appropriate precautions should be taken. This may include keeping fires away from galvanized structures or utilizing additional fire-resistant coatings or materials when necessary.
In summary, understanding how fire affects galvanized coatings is crucial for ensuring safety in construction projects.